Receding Gums: Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
As we age, it’s common to notice that our gums start to recede, gradually exposing more of the teeth’s roots. In previous articles, we have discussed the importance of gum care and its impact on overall health. Receding gums can significantly affect both dental health and appearance, making it a periodontal concern that warrants attention. In this article, we explore the common causes of gum recession, along with preventive measures and various treatment options for severe conditions.
Understanding Receding Gums
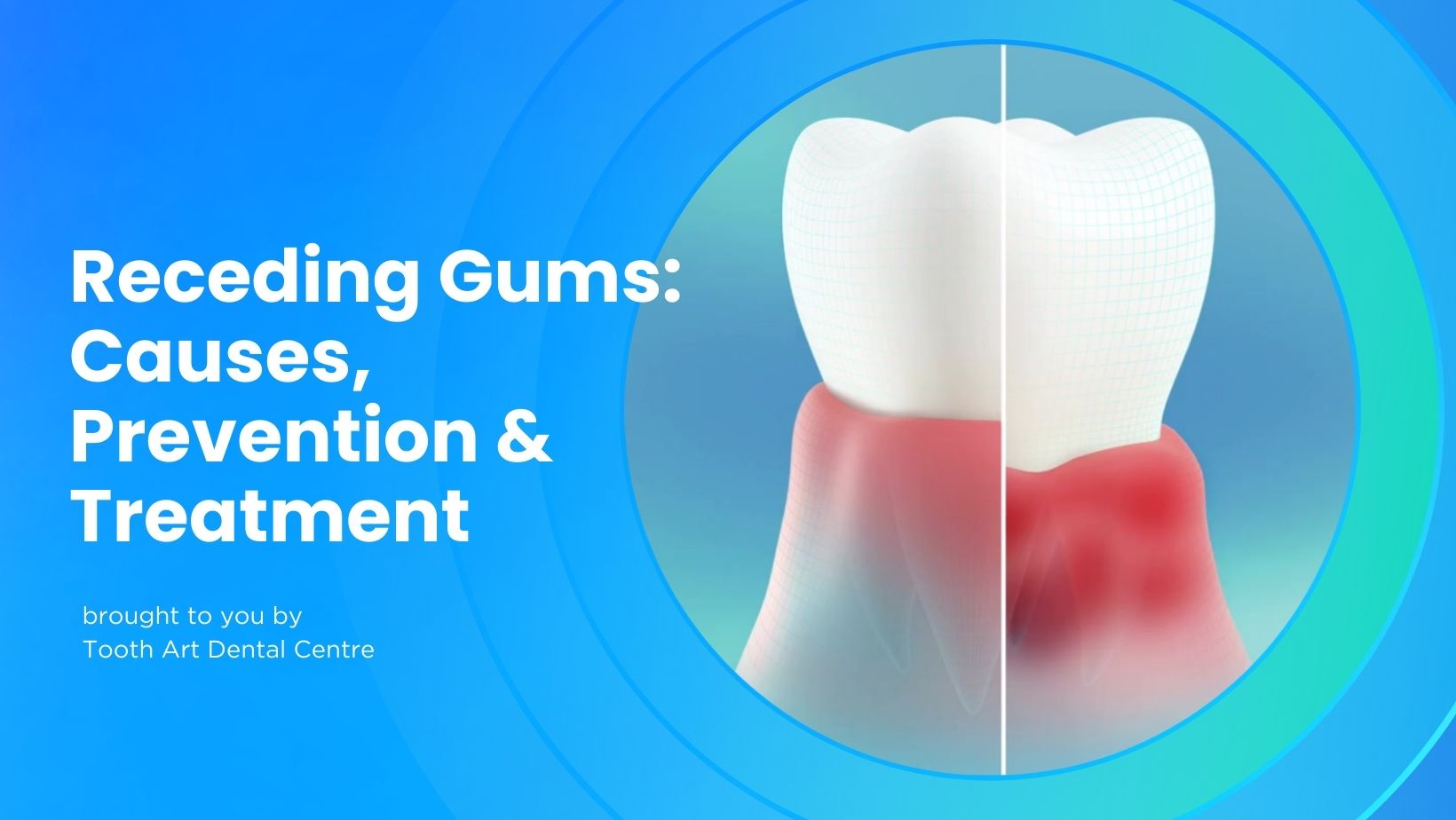
Receding gums, also known as gingival recession, is a condition where the margin of the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back. This process exposes more of the tooth or the tooth’s root, creating gaps between the teeth and gum line, making it easy for disease-causing bacteria to accumulate. Besides the aesthetic concerns, receding gums can lead to serious dental issues, including tooth loss.
Common Causes of Gum Recession
Several factors contribute to the development of receding gums:
- Overzealous Brushing: Brushing your teeth with too much pressure can wear down the enamel and cause the gums to recede. It’s recommended to use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle motions to clean the teeth effectively without harming the gums.
- Gum Disease: Periodontal diseases, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, are infections caused by bacteria that destroy gum tissue and the supporting bone that holds your teeth in place. Gum disease is the most common cause of gum recession.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Tobacco users are more likely to have sticky plaque on their teeth that is difficult to remove, which can lead to gum recession.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be more susceptible to gum disease, which in turn causes receding gums.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in female hormone levels during a woman’s lifetime, such as during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can make gums more sensitive and more vulnerable to gum recession.
- Misaligned Teeth or Grinding: Crooked teeth or a misaligned bite can put too much force on the gums and bones, leading to recession. Similarly, grinding or clenching your teeth can exert excessive force.
Why Gum Recession Is a Cause for Concern
The gums protect and support the teeth and the bone structure. When they recede, this protection is lost, leading to increased sensitivity. Patients may feel short sharp pains when chewing or when drinking something cold. You will also be exposed to an increased risk of tooth decay due to higher susceptibility to plague bacteria retention along the gum lines. Many patients have aesthetic concerns over longer-looking teeth and fear losing the teeth as the gums continue to recede.
Unfortunately, once the gum tissue has receded, it does not grow back naturally.
Modern Procedures for Treating Receding Gums
For cases where the recession is severe or continues to progress, dental professionals can employ various surgical procedures to treat and restore gums:
- Open Flap Scaling and Root Planing: In this procedure, the dentist or periodontist will lift the gums away to remove the tartar buildup. After thorough cleaning, the gum tissue is secured back into place.
- Regeneration: If the bone supporting your teeth has been destroyed due to gum recession, a procedure to regenerate lost bone and tissue may be recommended. After removing the bacteria, a regenerative material such as a membrane, graft tissue, or tissue-stimulating protein is applied to encourage your body’s natural ability to regenerate bone and tissue.
- Soft Tissue Grafts: This is the most common procedure to treat gum recession. Tissue is taken from the palate or another source and added to the affected area to cover the exposed roots.
Preventing Gum Recession
Prevention is always better than cure, especially regarding gum recession. Apart from preventing gum disease, which is one of the causes of receding gums, here are some strategies to prevent this condition:
- Practise Good Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss your teeth regularly but gently. Using an electric toothbrush with pressure sensors can also help prevent brushing too hard.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Regular visits to the dentist for cleanings and checkups can help prevent gum disease and monitor any changes in your gums.
- Quit Smoking: Avoiding tobacco in all forms helps maintain healthier gums.
- Use Mouth Guards: If you grind your teeth, consider getting a custom-made mouth guard to protect your teeth and gums while you sleep.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help prevent gum disease and promote overall dental health.
In conclusion, while receding gums is a common issue, especially as we age, understanding its causes and prevention can help maintain healthy gums. For those already experiencing significant gum recession, modern dental treatments offer effective solutions. Remember, the best approach is always a proactive one, focusing on prevention and early intervention. Regular dental visits and good oral hygiene practices are key to keeping your gums healthy for life.
If you’re concerned about your gum health, schedule a consultation with a periodontist to discuss a treatment plan tailored to your needs.