Understanding Dental Pain: Types, Causes, Treatment and Prevention
Dental pain, often referred to as a toothache, is discomfort or pain in or around the teeth and jaws. Its severity can range from mild to severe and can be constant or intermittent. Understanding the types of dental pain, their causes and treatment options is crucial for effective management. Let’s first understand the structure of a tooth.
The Anatomy of a Tooth and the Role of Nerves
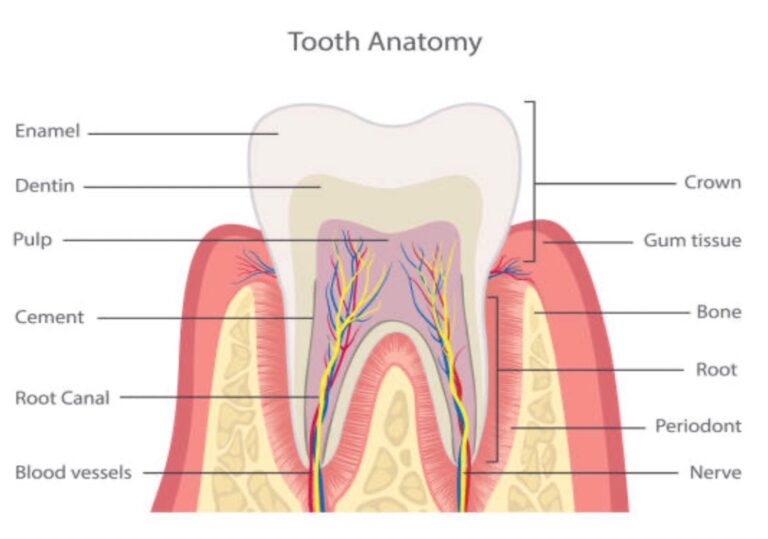
Inside each tooth, beneath the hard outer enamel and dentin layer, lies the pulp. This soft tissue is home to nerves and blood vessels, which provide the tooth with nutrients and sensation. It’s the stimulation of these nerves that typically leads to the experience of dental pain.
Types of Dental Pain
Dental pain can vary widely in terms of location, intensity, duration and underlying cause. These pain sensations include:
- Sharp and sudden pain: Intense and quick pain that occurs unexpectedly.
- Throbbing or pulsating pain: Continuous pain with a rhythmic beat-like sensation.
- Sensitivity to hot or cold: Pain triggered by temperature changes in foods or beverages.
- Pain with pressure or biting down: Discomfort when chewing or applying pressure to the tooth.
- Aching and soreness in the jaws or gums: General discomfort or soreness in one or more areas of the oral cavity.
- Chronic, dull ache: Persistent, low-level pain that lingers over time.
- Radiating pain: Pain that starts in one area and spreads to surrounding regions.
Causes of Dental Pain
- Tooth decay: The most common cause of dental pain, decay occurs when the enamel and dentin of a tooth become demineralized due to acids produced by bacteria in plaque.
- Tooth sensitivity: Sensitivity to hot, cold or sweet foods can cause discomfort, often due to exposed dentin, receding gums or thinning enamel.
- Gum disease (periodontal disease): Infections and inflammation of the gums can lead to pain and tooth sensitivity.
- Tooth abscess: An infection at the root of the tooth or between the gum and tooth causing severe pain and swelling.
- Tooth fracture: Crack(s) in a tooth can expose the sensitive inner layers, causing pain.
- Damaged fillings or dental work: Old or damaged fillings can expose sensitive parts of the tooth causing pain.
- Impacted wisdom tooth: Tooth that is blocked from emerging fully can cause pressure, pain and infection.
- Bruxism (teeth grinding): Grinding or clenching teeth, especially at night, can cause tooth, jaw and muscle pain.
- Misaligned teeth or jaw: Can lead to uneven pressure on teeth, causing chronic pain.
- Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMJ): Problems with the jaw joint and surrounding muscles can cause facial and dental pain.
- Sinusitis: Sometimes, pain in the upper teeth can be due to sinus inflammation or infection.
The Importance of Professional Evaluation
While over-the-counter painkillers can provide temporary relief, they are not a long-term solution. It is crucial to address the underlying cause of the pain. A skilled dental professional can accurately diagnose the cause of pain and recommend appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options
Treating dental pain effectively depends on the underlying cause. Treatment options include:
- Medications: This can include over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In cases of severe pain or infection, prescription painkillers and antibiotics may be necessary.
- Dental Fillings: Fillings are used to repair cavities and restore the integrity of a tooth. The decayed part of the tooth is removed and filled with materials like tooth-coloured composite resin to prevent further decay and restore function. A dental crown is usually recommended for a large cavity.
- Root Canal Therapy: In cases where tooth decay or damage has reached the pulp, a root canal is necessary. This procedure involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning the inside of the tooth, and sealing it to prevent further infection. A dental crown is usually recommended after root canal treatment to strengthen the tooth.
- Tooth Extraction: Sometimes, if a tooth is severely damaged or decayed, extraction may be the best solution followed by restoration options such as a dental implant, dental bridge or dentures to replace the extracted tooth.
- Gum Treatment: For toothaches caused by gum disease, periodontal cleaning and treatment are necessary.
Prevention: The Best Strategy
Preventing dental pain is far more effective than treating it after it occurs. This proactive approach involves several key components to maintain oral health.
Firstly, good oral hygiene requires regular brushing, flossing and the use of fluoride mouthwash to remove plaque and prevent tooth decay and gum disease.
Secondly, regular dental check-ups allow for early detection and treatment of potential problems before they become serious. Dentists can provide professional cleanings, identify areas of concern, and offer guidance on how to care for your teeth and gums effectively.
Thirdly, making healthy lifestyle choices such as a balanced diet low in sugary and acidic foods that can erode tooth enamel, avoiding tobacco products which contribute to gum disease and oral cancer, and limiting alcohol consumption.
Lastly, protecting your teeth from injury by wearing a mouthguard during sports and addressing any issues like teeth grinding can prevent pain and damage.
By integrating these practices into your daily life, you can significantly reduce the risk of dental pain. A healthy smile enriches your life.
Experiencing dental pain right now? It is time to seek professional help. Schedule a consultation for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Note:
This article is intended for informational purposes only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Individuals experiencing health concerns should consult with healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and treatment plans.